Abstract
Introduction
One of the strongest predictors of outcome in multiple myeloma (MM) patients are the intrinsic genetic abnormalities in the malignant plasma cells. t(14;16)(q32;q23) deregulates the c-musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma (c-MAF) oncogene. Due to the relative rarity of t(14;16) [<5% of newly diagnosed MM], there are no large databases which provide the natural history of this abnormality (the largest reported by Palumbo et al, R-ISS for MM: An IMWG Report included 84 patients).
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 213 patients with t(14;16) from 24 clinical centers in Germany, Italy, Spain, Israel, Poland, Romania, Czech Republic and the United States. Diagnosis and clinical responses were based on the International Myeloma Working Group criteria. The t(14;16) was detected by double color fluorescence in situ hybridization using bone marrow samples. Baseline characteristics at diagnosis, patient treatment and clinical outcomes were collected using unified forms. Overall survival (OS) was defined as the period between the date of diagnosis and the date of death or last observation. Progression-free survival (PFS) was defined as the period between the date of diagnosis and either the date of the first relapse, of the last observation or death of any causes. Cox proportional hazard regression analysis was applied to assess risk factors of death. Survival curves were plotted by the Kaplan-Meier method and compared using log-rank and Breslow-Gehan-Wilcoxon tests.
Results
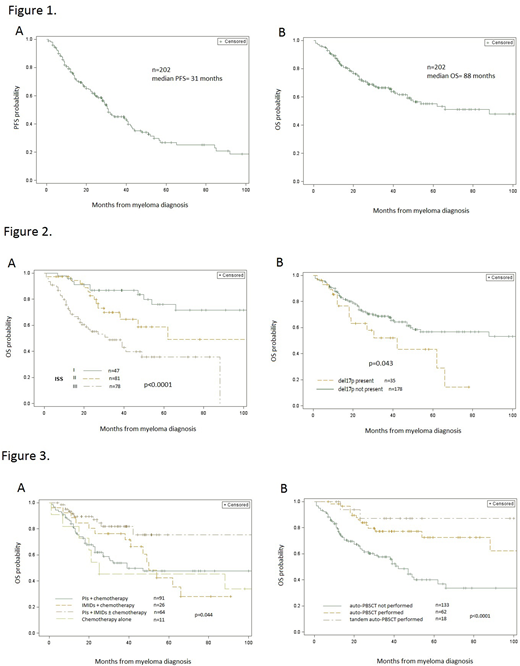
We analyzed a total of 213 patients, mean age 62.1 years (range 32 to 90), including 91 (42.7%) males. Immunoglobulin isotype included IgG (n=98, 46.0%), IgA (n=60, 28.2%) and IgM (n=1, 0.5%), light chain only in 47 cases (22.1%). ISS stage at diagnosis included: stage III (n=78, 36.6%), stage II (n=81, 38.0%) and stage I (n=47, 22.1%); for R-ISS: stage III (n=79, 37.1%), stage II (n=71, 33.3%), stage I (n=10, 4.7%). For stage is unknown for the remaining patients. Hypercalcemia was present in 38 cases (17.8%), anemia (<10g/dl) in 109 (51.2%) and impaired renal function (creatinine clearance <40 mL per minute or serum creatinine >2 mg/dl) in 54 (25.4%) patients. In 104 (48.8%) cases osteolytic lesions were present. The t(14;16) was associated with other aberrations in 134 (62.9%), in 35 (16.4%) patients with del17p. First line treatment for MM with t(14;16) included PIs + chemotherapy in 72 patients (36%), PIs + IMIDs in 39 patients (20%) or chemotherapy + PIs + IMIDs in 25 patients (13%).
Overall response rate was 67%. Median PFS was 31 months (CI 95% 28-40.3 months; Figure 1, panel A). Median OS was 88 months (CI 95% 49-177 months; Figure 1, panel B). 5-year OS from MM diagnosis was 55% (46-63%), whereas 10-year OS reached 44% (31-56%). Median OS for stage I was not reached, for stage II was 62 months (95%CI 38-177 months) and for stage III was 32 months (95% CI 18-88 months). Patients in ISS stage I had better OS than stage III patients (p<0.001; Figure 2, panel A). A total of 74 (34.7%) patients died. The causes of death included mostly disease progression in 28 cases (37.8%; 16 patients received ≥4 treatment lines) and infection in patients with progression in 21 cases (28.4%).
Patients treated with combined therapy of IMIDs, PIs ± chemotherapy had better survival than patients treated with IMIDs or PIs alone or chemotherapy alone (p=0.044; Figure 3, panel A). Patients after auto-PBSCT (median OS not reached, n=62, 29.1%), especially tandem auto-PBSCT (median OS not reached, n=18, 8.5%) performed better OS than patients without transplant (median OS: 42.1 months [95%CI 27- 62 months], p<0.0001, Figure 3, panel B).
Patients with additional del17p exhibited worse OS than patient with single t(14;16) mutation (median OS 42 vs 107 months, p=0.043; Figure 2, panel B).
Conclusion
This is the largest report of myeloma patients with t(14;16). Patients with t(14;16) and del17p had a worse prognosis than patients with t(14;16) alone. The use of auto-PBSCT, especially in the subgroup who received planned tandem auto-PBSCT, is associated with better survival. Combined therapy with PIs and IMIDs improved the overall survival in t(14;16) patients, which may suggests, that this high-risk prognostic feature might be partially overcome by the use of new-drug therapies. This study of 213 patients indicates that t(14;16) is not as severe adverse factor as compared to the original IMWG R-ISS analysis (n= 84), which suggests that the revised ISS may require updating.
Castillo:Genentech: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy, Research Funding; Millennium: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Beigene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding. Niesvizky:Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding. Rosinol Dachs:Janssen: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria. Cohen:Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Neopharm Israel: Consultancy, Honoraria; Medisson Israel: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Hari:Spectrum: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Kite Pharma: Consultancy, Honoraria; Sanofi: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria; Amgen Inc.: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Goldberg:COTA Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal